Rise In Hand Foot Mouth Disease (HFMD) Cases In Singapore
An alarmingly high number of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) cases has been recorded.
1,249 cases of HFMD were reported between 29 Jul and 4 Aug, a 1.5 times increase from 868 cases flagged the same period last year.
8 active clusters
8 kindergartens and childcare centres have been identified as active clusters of prolonged transmission — having had more than 10 HFMD cases or an attack rate exceeding 13%.
These schools also had transmission period of more than 16 days:
- Agape Little Uni @Compassvale
- Skool4kidz Campus @Sengkang Riverside
- My First Skool @2 Punggol Drive
- My First Skool @Blk 55 Toa Payoh Lorong 5
- My First Skool @682B Edgedale Plains
- PCF Sparkletots Preschool @Queenstown
- St James Church Kindergarten (Harding)
- Little Tree House Westwood Pte Ltd
Thankfully, none of them have been closed so far.
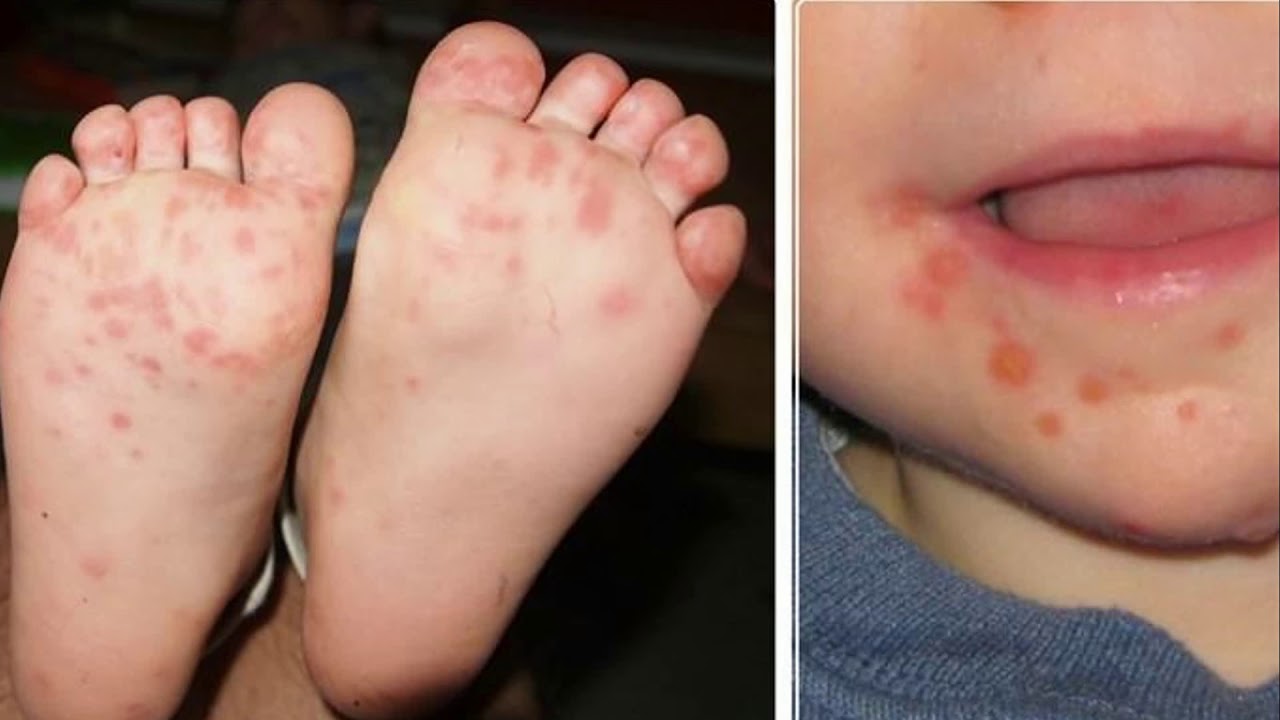
Although young children below the age of 5 are more susceptible to HFMD, adults can contract the disease too.
Be familiar with the symptoms
Best to familiarise yourself with the disease – its symptoms and means of transmission – to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Common symptoms of the virus include:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Mouth ulcers
- Rashes and blisters (hands & feet)
- Lethargy
- Poor appetite
Usually, HFMD is self-limiting. But severe cases involving the heart and nervous system may also occur.
No vaccines, but you can prevent the spread
There is no specific treatment against the virus, except to relieve the symptoms.
Nevertheless, most patients recover in 7-10 days.
No HFMD vaccinations are currently available, making it all the more important to prevent the spread of the virus.
Transmission via fluids through direct contact
HFMD spreads via direct contact with discharge from an infected person. These fluids include saliva, faeces, nasal discharge, and fluids from blisters or rashes.
The virus is much more contagious during the first week of infection. After which, it becomes less contagious as the illness resolves.
But that said, it’s better to take precautions nonetheless.
Take simple precautions please
Simple precautions in your daily routine can be taken to minimise the spread of the disease.
They include:
- Proper handwashing before eating & after visiting the loo
- Not sharing utensils and towels with others
- Covering your mouth when sneezing or coughing
- Seeking immediate medical attention when symptoms arise
A form of enterovirus
HFMD is caused by viruses from the Enterovirus family — the same family that Polioviruses and Hepatitis A belongs too.
There are 2 main forms of the virus that cause HFMD in Singapore.
They are the Enterovirus A-71 (EV-A71) and the Coxsackievirus type A strains.
 Coxsackievirus
Coxsackievirus
Source
Both strains, however, are hardy and can live on surfaces for months.
Recently, EV-A71 was responsible for the death of the 17-month-old & 2-year-old boy in Penang.
Thankfully, the EV-A71 is “still not so prevalent” in Singapore — but it’s been on the rise.
History of HFMD in Singapore
HFMD was first identified in Singapore in 1972.
Dr Tay Chong Hai, discovered a Coxsackie A16 strain in the poop of a patient with mouth ulcers and rashes.
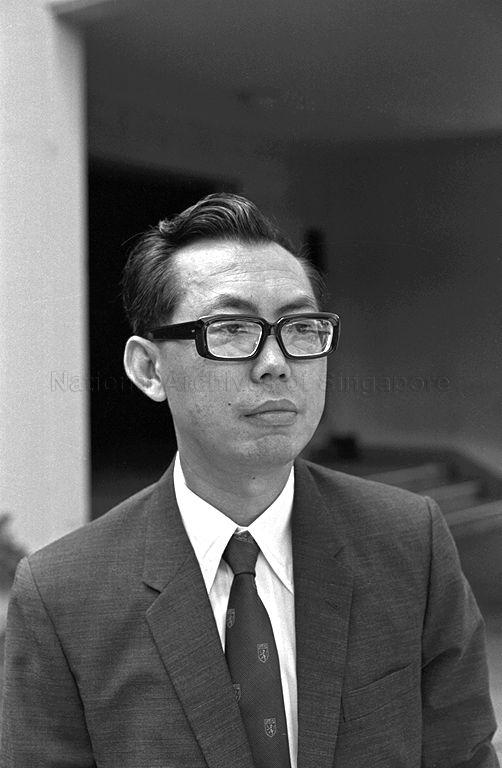 Dr Tay Chong Hai in 1972
Dr Tay Chong Hai in 1972
Source
Back then, there were only 104 cases over three months.
But in 2000, there was an outbreak of HFMD which caused the deaths of 7 children.
The incident led to HFMD being a legally notifiable disease, meaning your doctor must notify the Ministry of Health if they encounter a case of the virus.
Stay safe
With that, we wish all those infected with the virus a speedy recovery.
Featured image from KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital via Health Hub SG and The Disease Daily.