Older People & Patients With Underlying Illnesses Like Heart Disease Are Most At Risk From Covid-19
A Chinese study found that 80.9% of coronavirus cases are mild, but fatal cases may be triggered by pre-existing diseases.
On Tuesday (18 Feb), Channel NewsAsia (CNA) reports that patients most likely to die from Covid-19 complications were those with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, and hypertension.
The Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CCDC) concluded these findings based on 72,314 confirmed and suspected cases of Covid-19 in China.
As of Thursday (20 Feb), there are 74,577 cases and 2,118 deaths in the republic.
Most Covid-19 cases are mild
According to the study, 80.9% of infections were classified as mild. Meanwhile, 13.8% were classified as severe and only 4.7% were considered to be critical.
Concurrently, World Health Organisation (WHO) had also said on Tuesday (18 Feb) that the new novel coronavirus only causes mild disease for 80 per cent of infected patients.
WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus told reporters in Geneva,
It … appears that COVID-19 is not as deadly as other coronaviruses including SARS and MERS.
Although most Covid-19 infections are mild, things might not be the same for the elderly, and those with chronic illness, as we’ll soon find out below.
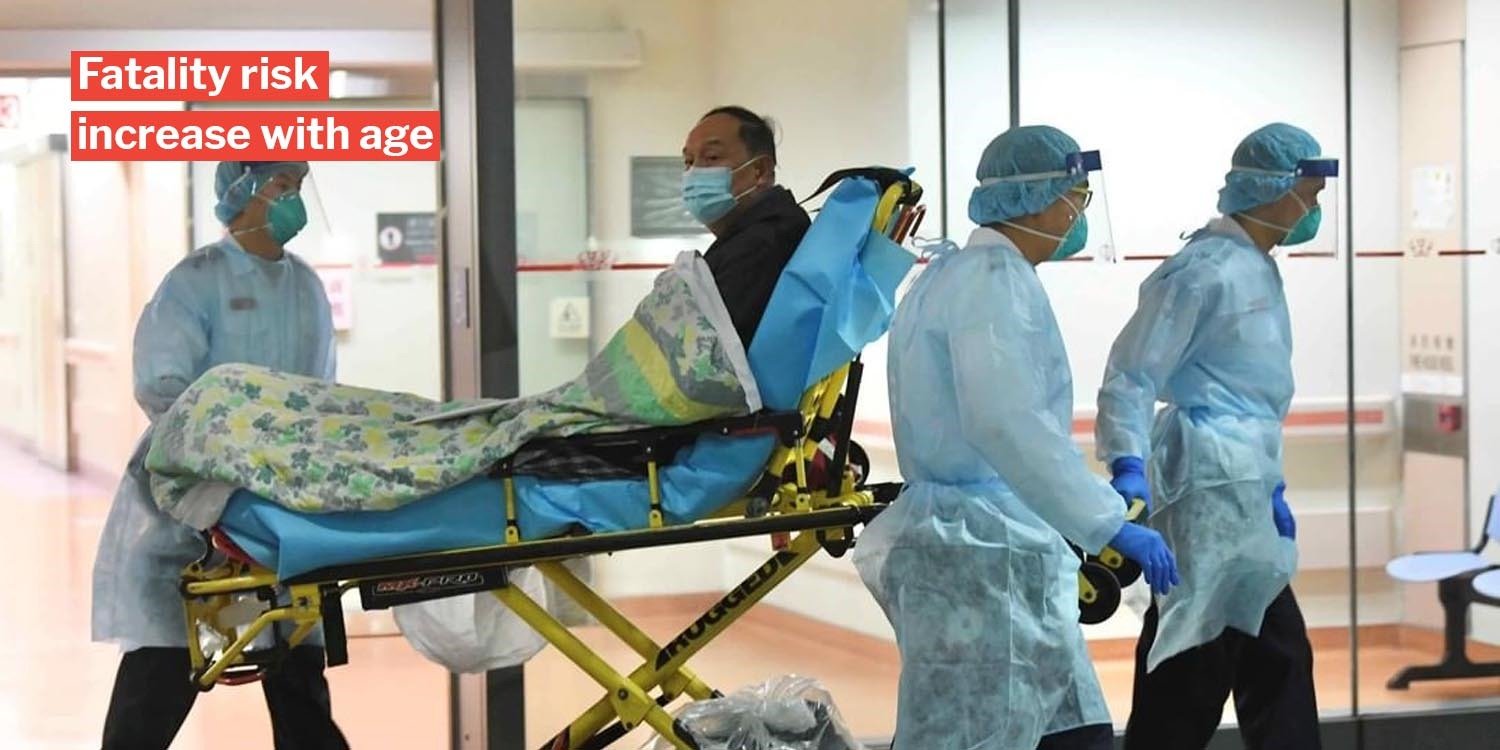
Fatality risk increases with age
The overall death rate from the virus is at 2.3%, and fatality risk increases gradually based on a patient’s age.
Here are the fatality rates per age group:
- 9 years old and below – no deaths
- Up to 39 years old – 0.2%
- 40 to 49 years old- 0.4%
- 50 to 59 years old – 1.3%
- 60 to 69 years old – 3.6%
- 70s to 79 years old – 8.0%
- 80 and older – 14.8%.
Hence, the elderly seem to be at most risk based on their high fatality rates.
If a patient had cardiovascular disease, the study finds that they are more likely to die from Covid-19.
The overall risk also increased for patients with diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, and hypertension.
In contrast, there were no deaths amongst children up to 9 years old. This includes 2 cases of Covid-19 detected on newborn babies who were infected in their mother’s womb.
Men were more likely to die (2.8 per cent) compared to women (1.7 per cent).
Spread of disease is slowing
The epidemic reached its “first peak” between Jan 24 and 26.
There was a “downward trend” since Feb 11 so the spread of the disease outside of Hubei province was slowing down.
Last Thursday (13 Feb), China expanded its definition of confirmed cases to include patients diagnosed through lung imaging.
The data shows that China’s decision to lockdown Hubei province played a significant role in preventing the spread of the virus.
Those with heart disease must stay alert
Scientists suspect that Covid-19 may adapt and become more deadly.
Hence, locals with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension should stay alert.
While we never know what the future holds, let’s hope that a vaccine will come soon.
Featured image adapted from Instagram.